In today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape, the convergence of Information Technology (IT) and Operational Technology (OT) is essential for optimizing processes, enhancing productivity, and maintaining a competitive edge. At Ultech Engineering, we understand the challenges industries face in integrating these two realms, and we believe that Edge Computing offers a powerful solution to bridge this gap effectively while fortifying cybersecurity.


Edge Computing involves processing data near the source of data generation rather than relying solely on centralized cloud-based systems. By bringing computation and data storage closer to the devices and sensors in the field, Edge Computing reduces latency, enhances real-time data processing, and improves the overall efficiency of industrial operations.

Traditionally, IT and OT have operated in silos. IT systems manage data-centric tasks such as enterprise resource planning (ERP), customer relationship management (CRM), and other administrative functions. In contrast, OT focuses on the monitoring and control of physical devices and processes on the factory floor, including machinery, sensors, and control systems.
The convergence of IT and OT is crucial for creating a unified infrastructure that supports seamless data flow and integrated operations. However, this convergence poses significant challenges, particularly in terms of ensuring robust cybersecurity and managing the vast amounts of data generated by industrial systems.
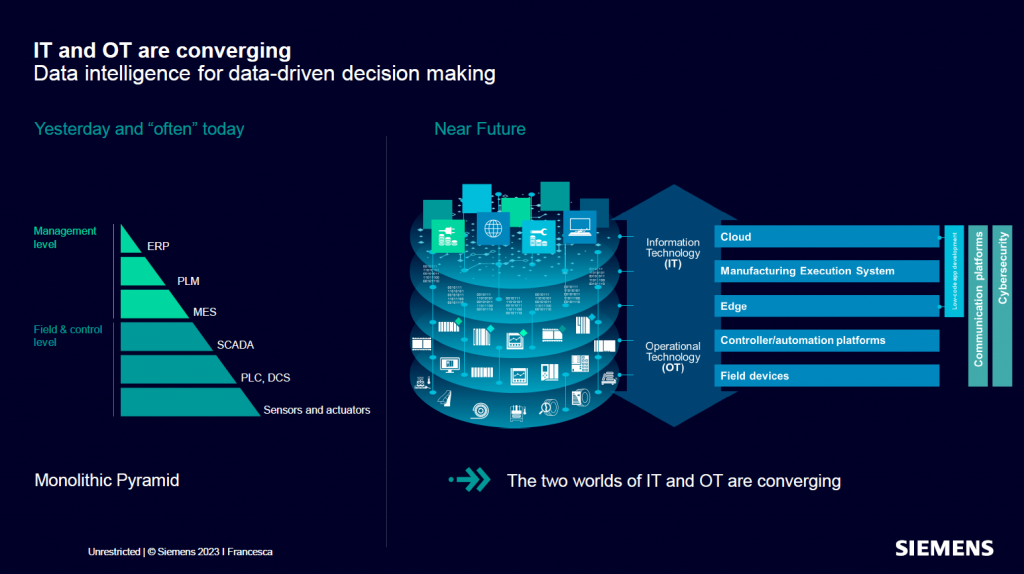
Edge Computing stands out as a transformative technology that facilitates the convergence of IT and OT, offering several compelling benefits:

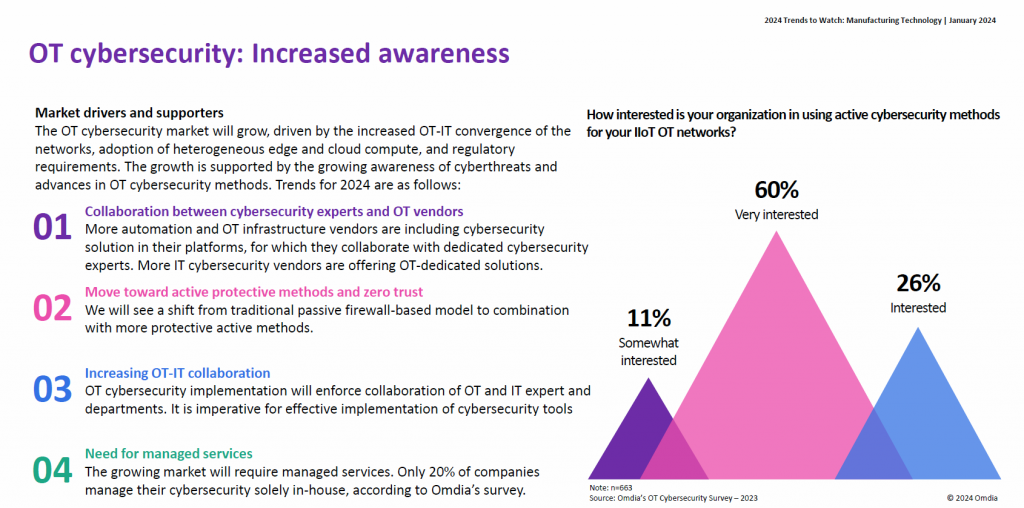
One of the most significant advantages of Edge Computing in industrial environments is the enhanced cybersecurity it offers. By processing data locally, Edge Computing minimizes the exposure of sensitive data to potential cyber threats during transmission. This localized approach provides several layers of security:
The Internet of Things (IoT) expansion is revolutionizing how data is collected, processed, and analyzed. Central to this growth are edge devices, which are becoming increasingly vital for IoT's success and continued evolution.
Edge devices facilitate data transmission between local networks and the cloud. They act as intermediaries, translating protocols used by local devices (such as Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, Zigbee, and NFC) into those used by the cloud (such as AMQP, MQTT, CoAP, and HTTP). This translation is essential for IoT data to move seamlessly between local devices and cloud services for further processing. Without edge devices, this data would be incompatible and unable to reach the cloud for deeper analysis. For instance, certain Edge devices work as security-conscious devices that can support multiple machines over a network or be installed near a single machine.
Edge devices come in various forms, each serving different functions within IoT and industrial IoT (IIoT) systems.
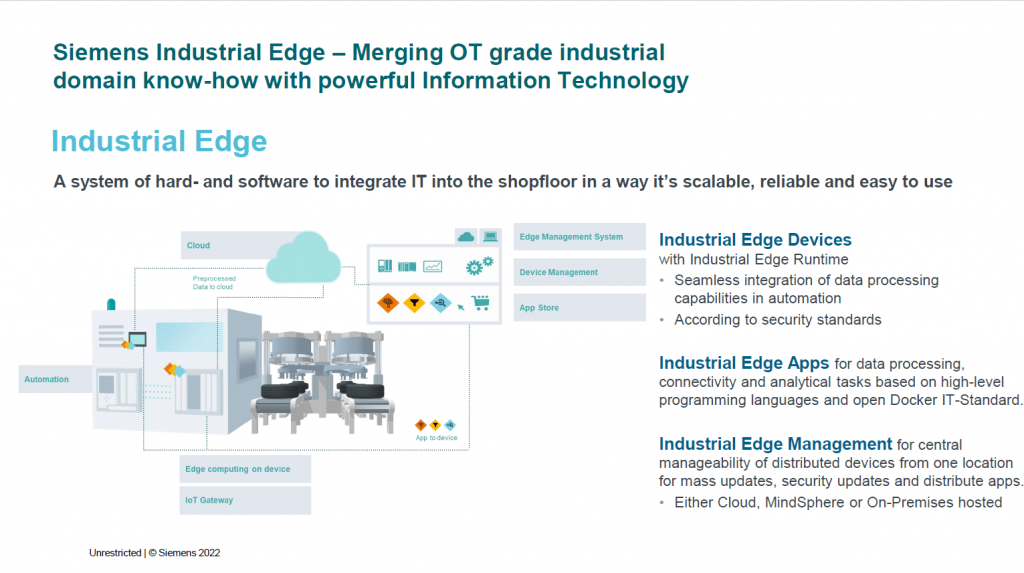
Edge devices operate near the data source, such as sensors, acquiring data and sending it to the cloud or processing it locally. They can manage data flow, perform real-time analysis, and trigger responses through actuators. In large systems, a combination of sensors, actuators, routers, switches, and edge devices work together to provide visibility and control over long distances.
Edge devices offer numerous advantages, including:
Edge devices have various applications, such as:
Edge devices are essential for modern IIoT implementations, offering reliable, low-latency solutions for local data analysis. They enable condition-based monitoring, prevent critical failures, and improve equipment uptime. By translating and transmitting data between local and cloud systems, edge devices provide real-time analysis while benefiting from robust cloud-based processing and storage.
Edge computing devices bridge the gap between local and cloud computing, offering manufacturers flexibility, reliability, and speed in a secure, cost-effective manner. They are crucial for creating digital twins of manufacturing facilities, managing data efficiently, enabling offline capabilities, and supporting complex event processing. Additionally, edge devices enhance AI and ML applications, providing real-time, autonomous decision-making and immediate business insights.

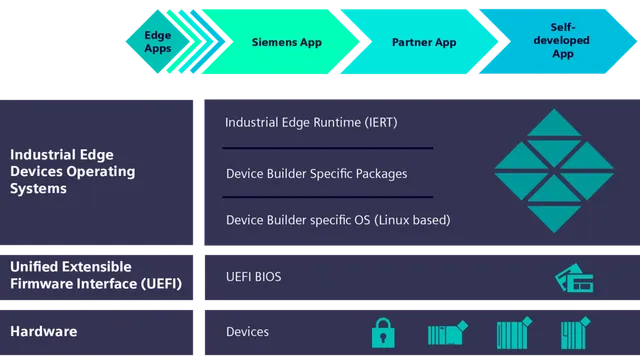
The Industrial Edge device architecture ensures industrial-grade security with features like no root access and secure boot enforcement. Maintenance is simplified through regular feature updates and bug fixes delivered via Industrial Edge, which also offers logging services. The system's quality and robustness meet industry standards, featuring an industrial-grade OS and comprehensive end-to-end system testing.
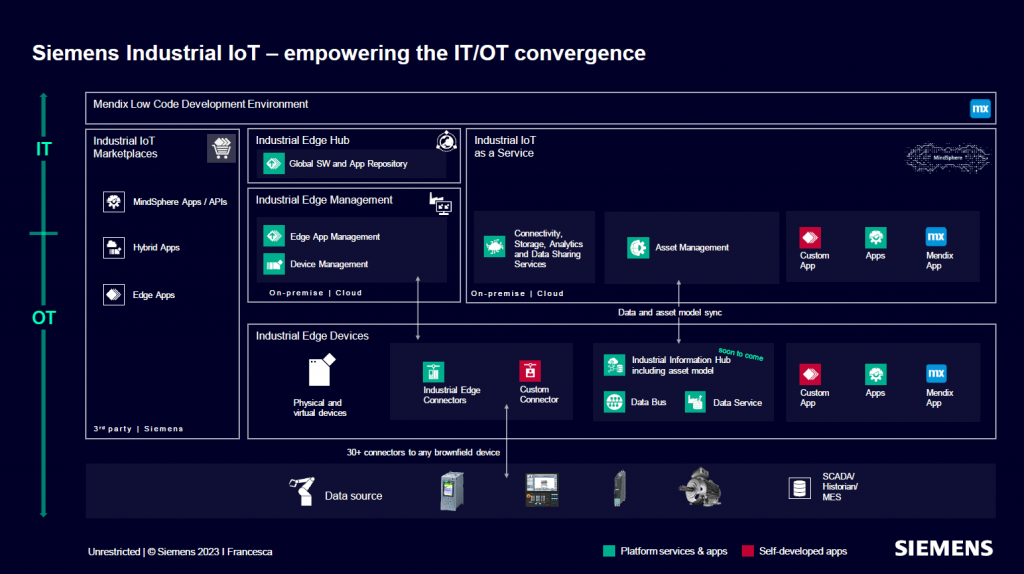
Siemens Industrial Edge is an open software platform from Siemens that ensures that manufacturing IT is simple, scalable, and easy to control. Out-of-the-box applications, software, and devices enable higher productivity and new business opportunities. The following Siemens Industrial Edge Devices are a good starting point for implementing edge computing in your production environment: You can employ virtualized systems and IPCs, use SIMATIC controllers and HMIs with integrated edge capability, and get certified edge devices from various partners in the Industrial Edge Ecosystem.
Siemens Industrial Edge IPCs are revolutionizing the industrial landscape by offering robust, high-performance solutions seamlessly integrating IT and OT systems. These maintenance-free devices, including the SIMATIC IPC127E, IPC227E, IPC227G, IPC427E, IPC847E, IPC BX-39A, and IOT2050, are designed for flexible deployment in demanding environments. With advanced features and unparalleled reliability, Siemens Industrial Edge IPCs enable efficient data processing and real-time analytics at the edge, driving digital transformation and enhancing operational efficiency in industrial applications.


Siemens Industrial Edge IPCs, with their advanced features and robust designs, are essential for achieving seamless IT/OT integration, driving efficiency, and ensuring high performance in industrial digitalization efforts. On top of that, Siemens also collaborates with other technology partners, such as our other principal partner, Weidmuller. Weidmuller EDGE Industrial PC Devices with u-OS are a contribution to the Industrial Edge Devices ecosystem. The uc20-M3000 and uc20-M4000, for example, combine the possibilities of Automation and Industrial IoT in one device. They are expandable and offer a web-based system structure with access to the Weidmuller software landscape and partner networks such as Siemens Industrial Edge.

Siemens SIMATIC HMI Unified Comfort Panels are Edge-enabled solutions that integrate visualization and data analysis into a single device, optimizing space in control panels. These advanced panels feature 768 MB of memory and 512 MB of storage dedicated to Edge applications. With interfaces including 2x RJ45 ports (each with separate IP addresses) and 4x USB 3.0 ports, they offer versatile connectivity options. The SIMATIC HMI Unified Comfort Panels streamline industrial operations by providing powerful, space-saving solutions for real-time data analysis and control.
Siemens Industrial Edge Software-based Devices provide flexible and scalable solutions for industrial applications without the need for dedicated hardware. The Industrial Edge Virtual Device (IEVD) offers full Industrial Edge functionality on standard virtualization platforms like ESXi/vSphere. It allows configurable resource allocation, including up to 8 virtual CPUs, 64 GB of RAM, and unlimited storage and network adapters. This virtual approach ensures a quick and easy start with the Industrial Edge experience, scalable as demand grows.
The Industrial Edge Own Device (IEOD) enables customers to run Industrial Edge functionalities on their preferred x86_64 hardware platforms. Once validated for compatibility, the system allocates available resources such as CPU, memory, disk space, and network interfaces to the Industrial Edge Runtime. This approach ensures functional compatibility with other Industrial Edge devices while offering a high security level for production environments. Leveraging third-party hardware helps lower entry barriers into the Industrial Edge ecosystem, providing unlimited CPU, memory, storage, and network adapter resources, subject to hardware capabilities and validation results.
Siemens Industrial Edge Industrial Switches bring advanced connectivity and computing capabilities to harsh industrial environments, enhancing network reliability and performance.

RUGGEDCOM APE1808 Edge Device: Designed for the RUGGEDCOM RX1500 series Multi-Service Platform, the RUGGEDCOM APE1808 is a robust application hosting platform that facilitates the integration of Edge computing applications into industrial networks. It features a fan-less operation and can withstand temperatures ranging from -40 °C to +75 °C. The device supports up to two APE modules within a single RX1500 series unit and can run on either Linux or Windows IoT Enterprise. Key features include an Intel Atom x5-E3940 CPU with 4 cores, approximately 8GB of RAM, around 80GB of storage, and interfaces like 2x USB 3.0, 1x micro-SDHC, Intel HD 500 (Display Port), and Intel HD Audio through Display Port.
SCALANCE LPE9413 (ARM64): The SCALANCE LPE9413 Industrial Edge Device is a compact, maintenance-free solution that combines high performance and robustness for industrial environments. It operates reliably in temperatures from -40 °C to +60 °C and features a fan-less design with a redundant power supply. The device is equipped with the latest ARMv8 4-core CPU, approximately 3GB of RAM, and about 31GB of storage, expandable via an industrial 32GB CLP or a conventional USB interface. Interfaces include 2x 10/100/1000 Mbps RJ45 ports, 1x Combo-Port (10/100/1000 Mbps RJ45 or 100/1000 SFP), 1x USB 3.0, and 1x CLP. The SCALANCE LPE9413 can operate as a stand-alone unit or dock into a SCALANCE XCM-300 switch, providing flexible integration options without additional cables.
At Ultech Engineering, we recognize that the future of industrial operations lies in the seamless integration of IT and OT, driven by the power of Edge Computing. By adopting Edge Computing, local industries can achieve real-time data processing, reduced latency, enhanced reliability, scalability, cost efficiency, and robust cybersecurity. This technology addresses the complexities of IT-OT convergence and paves the way for a smarter, more efficient, and more secure industrial environment.
Join us on this journey towards digital transformation and discover how Edge Computing can revolutionize your industrial operations, ensuring that you stay ahead in a competitive market while safeguarding your critical assets. Embrace the future with Ultech Engineering and unlock the full potential of your industrial ecosystem.
Industrial Edge refers to deploying edge computing technologies specifically within industrial environments, such as manufacturing plants, oil refineries, or energy grids. The focus is on bringing computation, storage, and networking closer to industrial processes to improve efficiency, safety, and performance.
Intelligent Edge is a broader concept that encompasses the deployment of edge computing capabilities with advanced analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence (AI) at the edge of the network. This can be applied across various industries, not just industrial environments.
The key differences between Industrial Edges and Intelligent Edges can be found in these areas:
In summary, while Industrial Edge is a subset focused on enhancing industrial processes through edge computing, Intelligent Edge encompasses a broader range of applications with an emphasis on advanced analytics and AI, applicable to various industries and scenarios.