In the realm of industrial manufacturing, innovation has always been the driving force behind progress. From assembly lines to advanced robotics, the industry has continually evolved to meet the demands of an ever-changing world. Industrial automation is at the forefront of this evolution, a revolutionary concept that has transformed the manufacturing landscape and paved the way for a new era of efficiency and productivity.
Industrial automation, simply put, refers to the use of technology and control systems to streamline and optimize manufacturing processes. This includes everything from automated machinery and robotics to sophisticated control systems and software. The goal? To minimize human intervention, reduce errors, and maximize output, ultimately driving down costs and increasing competitiveness.

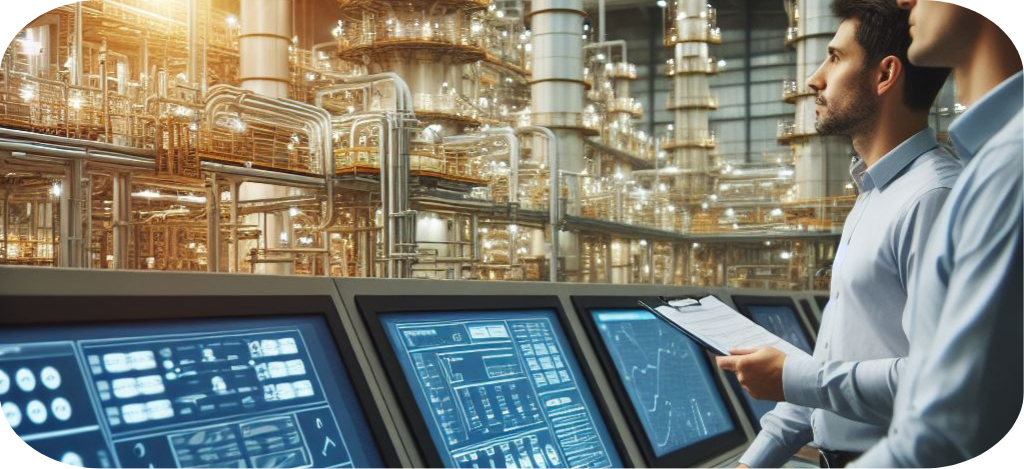
The impact of industrial automation on manufacturing cannot be overstated. By automating repetitive tasks and processes, companies can achieve levels of precision and efficiency that were once thought impossible. From automotive assembly lines to food processing plants, automation has revolutionized the way goods are produced, leading to faster production times, higher quality products, and increased safety for workers.
But perhaps most importantly, industrial automation has opened up new possibilities for innovation and growth. With the ability to collect and analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, manufacturers can make more informed decisions, optimize production schedules, and even predict maintenance issues before they occur. This level of insight not only improves operational efficiency but also enables companies to stay ahead of the competition in an increasingly competitive marketplace.
For illustration purposes, the following paragraphs are a few examples of industrial automation solutions, while the possibilities are virtually limitless. Industrial automation continues evolving with technological advancements, including robotics, AI, machine learning, and connectivity, driving efficiency, productivity, and safety improvements across industries.

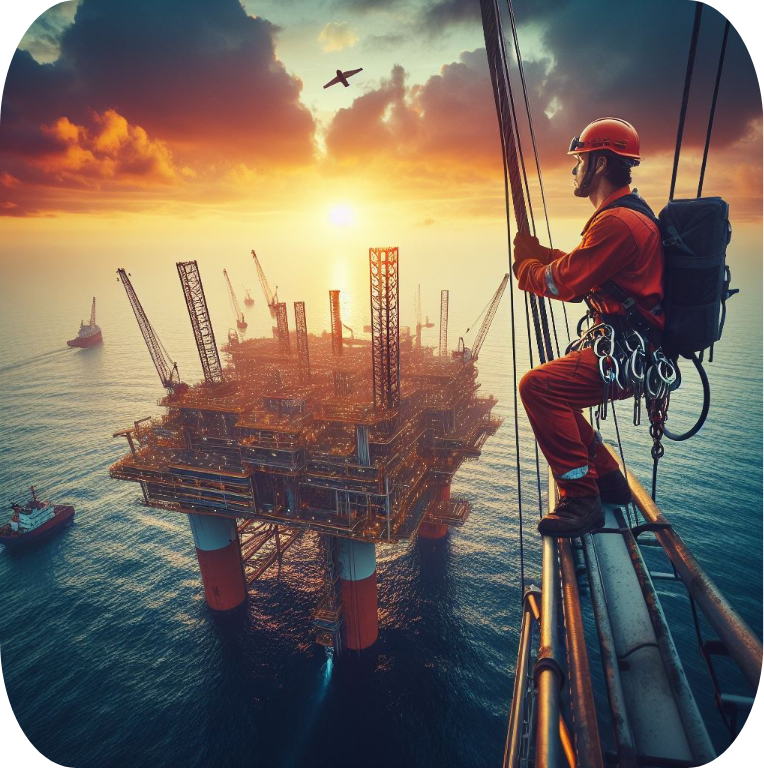
Ultech Engineering's past portfolio examples of industrial automation projects can also be referred to in two articles here and here. The former link features automation projects in oil and gas, while the latter link features automation projects completed in other and general industries.

As technology advances, we are witnessing the emergence of a new wave of industrial automation: the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and Intelligent Edges. This next-generation technology is taking automation to new heights, providing unprecedented connectivity, intelligence, and processing power.

IIoT refers to the network of interconnected devices, sensors, and systems that collect and exchange data in industrial settings. By harnessing the power of IIoT, manufacturers can create smart, connected factories that are capable of self-optimization and self-diagnosis. This enables real-time monitoring of equipment and processes, predictive maintenance, and seamless integration with other systems and platforms.

Intelligent Edges, on the other hand, bring the processing power of the cloud closer to the point of data generation. By processing data locally at the edge of the network, companies can reduce latency, minimize bandwidth usage, and improve overall system performance. This is particularly important in industrial settings where real-time responsiveness is critical.
Industrial connectivity refers to the integration and communication between various industrial devices, systems, and processes through interconnected networks. Automation plays a crucial role in industrial connectivity by enabling seamless data exchange and interoperability between different components of industrial systems. Here are some specific issues in industrial connectivity that automation can address:

By addressing these issues, automation can unlock the full potential of industrial connectivity, enabling smarter, more efficient, and more resilient industrial operations.


In this rapidly evolving landscape, the role of Automation and Control Engineers has never been more important. These highly skilled professionals are responsible for designing, implementing, and maintaining the systems that drive industrial automation. From programming PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) to configuring SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems, Automation and Control Engineers play a vital role in ensuring the smooth operation of automated manufacturing processes.
But their responsibilities extend beyond just technical expertise. Automation and Control Engineers must also possess strong problem-solving skills, a deep understanding of manufacturing processes, and the ability to collaborate effectively with cross-functional teams. As the guardians of industrial automation, they are tasked with continuously optimizing and improving processes to drive greater efficiency, productivity, and innovation.
At Ultech Engineering, we understand the importance of industrial automation and the critical role that Automation and Control Engineers play in shaping the future of manufacturing. With our expertise in automation solutions and commitment to innovation, we are dedicated to empowering the next generation of engineers to embrace the opportunities and challenges of the digital age.
As we look to the future, one thing is clear: the possibilities are endless. By embracing the power of industrial automation and harnessing the potential of IIoT and Intelligent Edges, we can unlock new levels of efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness, ensuring a brighter future for the manufacturing industry and beyond.